What is Unique Key
Unique key in Oracle Uniquely identifies every row in the database. It basically enforces uniqueness on the column defined
Important things
- There can be more than one Unique key per table
- It can be defined on one or more columns
- Columns comprising Unique key may be null-able
How to create the Unique Key
Table Creation
It can be done at Column Level with create table command in oracle
SQL> CREATE TABLE DEPT_MASTER (
dept_nr NUMBER UNIQUE,
dept_name varchar2(100) NOT NULL,
dept_status NUMBER(1,0) NOT NULL,
created_at date
);
Table created.
SQL> column CONSTRAINT_NAME format a20
SQL> column TABLE_NAME format a20
SQL> column INDEX_NAME format a20
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,TABLE_NAME,
INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints where
TABLE_NAME='DEPT_MASTER';

It can be done at the table level also
SQL> CREATE TABLE DEPT_MASTER (
dept_nr NUMBER ,
dept_name varchar2(100) NOT NULL,
dept_status NUMBER(1,0) NOT NULL,
created_at date,
Unique(dept_nr) );
Table created.
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,TABLE_NAME,
INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints where
TABLE_NAME='DEPT_MASTER';

We can provide the custom constraint also
SQL> CREATE TABLE DEPT_MASTER (
dept_nr NUMBER ,
dept_name varchar2(100) NOT NULL,
dept_status NUMBER(1,0) NOT NULL,
created_at date,
constraint DEPT_UK Unique(dept_nr)
);
Table created.
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,TABLE_NAME,
INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints
where TABLE_NAME='DEPT_MASTER';
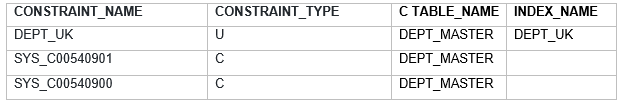
We can represent the Unique key with below diagram
We can have multiple column i.e composite Unique key also and it is defined at the table level only
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER_DETAIL
(
CUSTOMER_ID NUMBER(6,0),
NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL,
AGE NUMBER(6,0) NOT NULL,
ADDRESS VARCHAR2(25),
SALARY NUMBER(6,0),
UNIQUE(CUSTOMER_ID, NAME)
);
Table Created.
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,
TABLE_NAME,INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints where
TABLE_NAME='CUSTOMER_DETAIL';
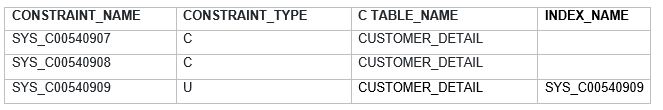
We can give custom constraint name also
SQL> CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER_DETAIL(
CUSTOMER_ID NUMBER(6,0),
NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL,
AGE NUMBER(6,0) NOT NULL,
ADDRESS VARCHAR2(25),
SALARY NUMBER(6,0),
constraint CUSTOMER_UK UNIQUE(CUSTOMER_ID, NAME)
);
Table created.
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,
TABLE_NAME,INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints where TABLE_NAME='CUSTOMER_DETAIL';
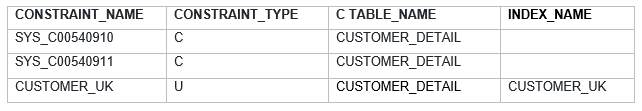
Alter Table add unique key
We can also add Unique key after table creation.Lets see the example of that
SQL> CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER_DETAIL(
CUSTOMER_ID NUMBER(6,0),
NAME VARCHAR (20) NOT NULL,
AGE NUMBER(6,0) NOT NULL,
ADDRESS VARCHAR2(25),
SALARY NUMBER(6,0)
);
Table created.
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,
TABLE_NAME,INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints where TABLE_NAME='CUSTOMER_DETAIL';
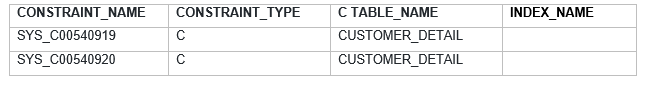
SQL> alter table customer_detail add constraint
customer_uk UNIQUE(CUSTOMER_ID, NAME);
Table altered.
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,TABLE_NAME,INDEX_NAME from user_Constraints where TABLE_NAME='CUSTOMER_DETAIL';
Primary Key and Unique key Both
We can have both the Primary key and Unique key on the oracle table.Here is the example demonstrating it
SQL> CREATE TABLE DEPT_MASTER (
dept_nr NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
dept_name varchar2(100) UNIQUE,
dept_status NUMBER(1,0) NOT NULL,
created_at date
);
Table created.
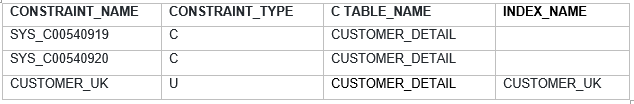
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,CONSTRAINT_TYPE,
TABLE_NAME,INDEX_NAME from
user_Constraints where TABLE_NAME='DEPT_MASTER';
How to find column associated with Unique key
We can find the column associated with Primary key or unique key from the dictionary view User_cons_columns
SQL> CREATE TABLE DEPT_MASTER (
dept_nr NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,
dept_name varchar2(100) UNIQUE,
dept_status NUMBER(1,0) NOT NULL,
created_at date
);
Table created.
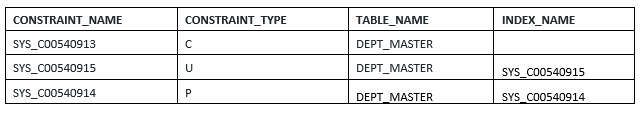
SQL> select CONSTRAINT_NAME,
CONSTRAINT_TYPE,TABLE_NAME,INDEX_NAME
from user_Constraints where TABLE_NAME='DEPT_MASTER';

SQL> SELECT Constraint_name, Table_name, Column_name FROM User_cons_columns where CONSTRAINT_NAME ='SYS_C00540915';
CONSTRAINT_NAME TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME
-------------------- ----------- ------------
SYS_C00540915 DEPT_MASTER DEPT_NAME
SQL> SELECT Constraint_name, Table_name, Column_name
FROM User_cons_columns where CONSTRAINT_NAME ='SYS_C00540914';
CONSTRAINT_NAME TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME
------------- --------- ---------
SYS_C00540914 DEPT_MASTER DEPT_NR
SQL> SELECT Constraint_name, Table_name, Column_name
FROM User_cons_columns where CONSTRAINT_NAME ='SYS_C00540918';
CONSTRAINT_NAME TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME
------------- ---------- ------------
SYS_C00540918 CUSTOMER_DETAIL CUSTOMER_ID
SYS_C00540918 CUSTOMER_DETAIL NAME
How to enable & disable the Unique key constraint
We can do this with alter table command. We can either provide the column name or the constraint name
SQL> alter table customer_detail disable UNIQUE(CUSTOMER_ID, NAME); Table altered. SQL> alter table customer_detail disable constraint CUST_UK; Table altered. SQL> alter table customer_detail enable UNIQUE(CUSTOMER_ID, NAME); Table altered. SQL> alter table customer_detail enable constraint CUST_UK; Table altered.
How to drop the Unique constraint
We can do this with alter table command. We can either provide the column name or the constraint name
SQL> alter table customer_detail drop UNIQUE(CUSTOMER_ID, NAME); Table altered. OR SQL> alter table customer_detail drop constraint CUST_UK; Table altered.
Hope you like this detail on Unique key in Oracle. We have given enough examples for demonstrative purpose also. Please do provide the feedback on it
Also Reads
Oracle database Administration Tutorials
How to Add primary key in oracle : primary key uniquely identify the row in the table. How to Add primary key in oracle, how to drop primary key, how to create composite key
https://asktom.oracle.com/pls/asktom/f%3Fp%3D100:11:0::::P11_QUESTION_ID:5541352100346689891