We are bringing here a compilation from Must Read Top 100 Hyperion Essbase Interview Questions.
1) What is Essbase?
Answer
Essbase stands for Extended Spreadsheet Database. Essbase is a multidimensional database Management System(MDBMS) that provides a multidimensional database platform upon which to build Analytical Applications. Essbase products provide companies with the ability to deliver critical business information to the right people when they need it. Essbase products can be deployed on the web with minimum infrastructure requirements. The Essbase Server client needs only to retrieve and view data that resides on a server.
Essbase maintains the Hierarchical data structure. The server acts as a shared resource, handling all data storage, caching, calculations, and data security.
2) What is Dimension?
Answer A dimension represents the highest consolidation level in the database outline. The database outline presents dimensions and members in a tree structure to indicate a consolidation relationship
3) What are Members?
Answer Members are the individual components of a dimension.
Each member has a unique name. Essbase can store the data associated with a member.
4) what are standard dimensions?
Answer
They represent the core components of a business plan and often relate to departmental functions. Typical standard dimensions are Time, Accounts, Market, and Division. Storage space is allocated to standard dimensions and Essbase maximizes performance by dividing the standard dimensions of an application into two Types: dense and sparse dimensions.
5) What are dense dimensions?
Answer
It is a dimension with a high probability that data in one or more cells are occupied in every combination of dimensions. Like Period and Account.
6) What are Sparse dimensions?
Answer It is a dimension with a low probability that data in one or more cells are occupied in some combination of dimensions. Like product because
All the products may not be sold in all areas of the country
7) What are Attribute dimensions?
Answer
They are a special type of dimension that is associated with the standard dimension. The standard dimension is the base dimension for that attribute dimension.
Attributes describe characteristics of data such as the size and color of products. Through attributes, you can group and analyze members of dimensions based on their characteristics.
8) What are the types of Partitions available in Essbase?
Answer
Three types of partitions are there.
| Transparent partition | A form of shared partition that provides the ability to access and manipulate remote data transparently as though it is part of your local database. The remote data is retrieved from the data source each time you request it. Any updates made to the data are written back to the data source and become immediately accessible to both local data-target users and transparent data-source users |
| Replicated Partition: | A form of partition where data is copied from a remote source to a local database |
| Linked Partition: |
9) What is the difference between standard and attribute dimensions?
Answer
| Standard Dimension | Attribute dimensions |
| Essbase Allocate storage for Standard dimensions’ members. | Essbase does not Allocate Storage for Attribute dimensions’ members. Instead, it dynamically calculates the members when the user requests data associated with them. |
| UDA members are allowed | Not allowed |
| Shared members are allowed | Not allowed |
| It must be associated with Base dimensions |
9) What are the two storage options available in Essbase and what are the differences?
Answer
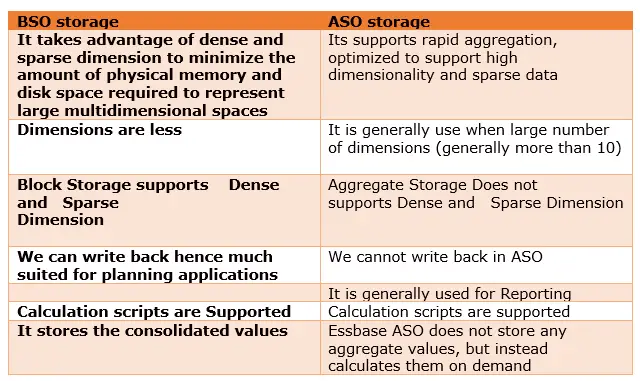
10) How is data stored in the Essbase database?
Answer
Essbase is a file-based database where the data is stored in PAG files of 2 GB each and grows sequentially.
11) How does UDA’s impact database size?
Answer
Absolutely no impact as UDA’s does not require additional storage space.
12) What is the difference between UDA’s and Attribute dimensions?
Answer
Attribute dimensions provide more flexibility than UDA’s. Attribute calculation dimensions which include five members with the default names sum, count, min, max, and avg are automatically created for the attribute dimensions and are calculated dynamically.
13) What are rules files?
Answer
It defines operations that Essbase performs on data values or on dimensions and members when it processes a data source. We use rules to map data values to an Essbase database or to map dimensions and members to an Essbase outline.
14) Is it possible to have multiple databases in one single application?
Answer
Yes. However, only one database per application is recommended.
15) Is it possible to have one ASO database and one BSO database in one single application? If yes, how and If No, why?
Answer
No. Because we define the ASO or BSO option while creating the application and not the database. Hence if the application is ASO, the databases it contains will be that type only.
16) What are the file extensions for an outline, rule file, and calculation script.
Answer
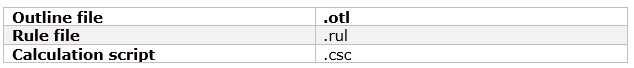
17) What is the role of analytics provider services?
Answer
Analytics Provider Services is used to communicate between Essbase and Microsoft Office tools (Smart View)
18) How do Attribute dimensions and UDAs impact batch calculation performance?
Answer
UDA’s- No Impact as they do not perform any inherent calculations.
Attribute dim- No Impact as they perform only dynamic calculations.
19) How can we display UDAs in reports? How do they impact report performance?
Answer
UDA’s values are never displayed in the reports and hence do not impact report performance.
20) How does Attribute dim impact report performance?
Answer
They highly impact the report performance as the attributes are calculated dynamically when referenced in the report. For a very large number of att dim displayed in the report, the performance could drastically reduce.
21) What are the three primary building methods for building dimensions?
Answer
- Generation references
2. level references
3. Parent-Child references.
22) Can we build dimensions directly from data sources without using rule files?
Answer
No.
23) What is a block locking system?
Answer
Analytic services (or Essbase Services) lock the block and all other blocks that contain the Childs of that block while calculating this block is the block locking system.
24) What is a data file cache?
Answer
A buffer in memory that holds compressed data (.PAG) files.
25) What is a custom-defined function?
Answer Essbase calculation functions that you develop in the Java programming language and then add to the standard Essbase calculation scripting language by means of MaxL.
26) Can we start and stop an application individually? How can this be used to increase performance?
Answer
Yes. We can manage our server resources by starting only the applications that receive heavy user traffic. When an application is started, all associated databases are brought to the memory.
27) What are LRO’s( Linked Reporting Objects)?
Answer
They are specific objects like files, cell notes, or URLs associated with specific data cells of the Essbase database. You can link multiple objects to a single data cell. These linked objects are stored in the server. These LROs can be exported or imported into the database for backup and migration activities.
28) What is UDA (user-defined attributes)? How are they different from Aliases?
Answer UDA represents the class of the members. Aliases are just another name for the members. both are different and have different uses.
29) Can we query a member for its UDA in a calculation script?
Answer
Yes. You can query a member for its UDA in a calculation script.
30) While loading the data, you have applied both the selection criteria as well as rejection criteria to the same record. What will be the outcome?
Answer
The record will be rejected.
31) What is hybrid analysis?
Answer
Lower-level members and associated data remain in the relational database whereas upper-level members and associated data reside in the Essbase database.
32) How to create an Essbase application?
Answer
a) Open Essbase Administrative Services 11.1.12.
b) Enter the username and password to Logon into the Administration Server.
c) Inside Essbase select Application and then select Create application,
d) Either Block or Aggregate and name it.
e) Select the application and choose the option to create the DATABASE And name it.
f) Select “outline à Edit”
g) Using the left click select “Add Child”. Similarly, add required child and sibling as required and configure dimension and member property.
h) database and using left click “Create à Rule File”.
e) Select that database and using the left click “load data à Select data file and rule file”
33) What are the different types of attributes?
Answer
Essbase supports two different types of attributes.
1. User-Defined attributes
2. Simple attributes
User-defined attributes: The attributes that are defined by the user.
Simple attributes: Essbase supports some attributes, which are: Boolean, date, number, and string.
34) What are filters?
Answer
A method of controlling access to database cells in Essbase. A filter is the most detailed level of security, allowing you to define varying access levels different users can have to individual database values.
35) Why is top-down calculation less efficient than bottom-up calculation? Being less efficient, why do we use them?
Answer
In the process, it calculates more blocks than is necessary. Sometimes it is necessary to perform top-down calculations to get the correct calculation results.
36) What does never consolidate operator (^) do?
Answer
It prevents members from being consolidated across any dimension.
37) What are the different types of LOG Files?
Answer
The important log files are
1. Application log
2. Essbase.log
3. Configtool.log
4. eas_install.log
5. essbaseserver-install.log
6) opmn.log
7) Essbase_odl.log
38) What is TB First and TB Last?
Answer
TB First: in the Sample Basic database, the accounts member Opening Inventory is tagged as TB First. Opening Inventory consolidates the value of the first month in each quarter and uses that value for that month’s parent. For example, the value for Qtr1 is the same as the value for Jan.
TB Last: in the Sample Basic database, the accounts member Ending Inventory is tagged as TB Last. Ending Inventory consolidates the value for the last month in each quarter and uses that value for that month’s parent. For example, the value for Qtr1 is the same as the value for Mar.
39) How do you optimize the outline?
Answer
Usually, the outline is optimized using the hourglass design for dimension ordering i.e.,
· Dimension with Accounts tag
· Dimension with Time tag
· Largest Dense dimension
· Smallest dense dimension
· Smallest Sparse dimension
· Largest Sparse dimension
40) What are the ways to improve performance during data loads?
Answer
There are several ways to optimize the load
- Grouping of Sparse member combinations
2. Making the data source as small as possible
3. Making source fields as small as possible
4. Positioning the data in the same order as the outline
5. Loading from Essbase Server
6. Managing parallel data load processing
41) What are the design considerations for calculation optimization?
Answer
You can configure a database to optimize calculation performance. The best configuration for the site depends on the nature and size of the database.
· Block Size (8Kb to 100Kb) and Block Density
· Order of Sparse Dimensions
· Incremental Data Loading
· Database Outlines with Two or More Flat Dimensions
· Formulas and Calculation Scripts
42) What is SmartView?
Answer
It is a Web-deployed thin client that is embedded in a client spreadsheet application and Enables you to retrieve data and create ad hoc reports and it Provides integration with Microsoft Office products. This provides a single Excel interface to analyze data
43) What is an outline?
Answer
The outline is a Tree structure for dimension hierarchies and it also contains Consolidations and mathematical relationships between members
44) What are the applications and databases in Essbase?
Answer
| Applications
| Contains databases and shared scripts Reside on the server where the Essbase Server is installed Run application server processes |
| Databases
| Are repositories for multidimensional analytic data Contains database objects and security definitions |
45) We have created an application in Unicode mode. Can we change it later to non-Unicode mode?
Answer No.
46) What are the specified roles other than Administrator to view sessions, disconnect sessions, or kill users’ requests for a particular application?
Answer You should have the role of Application manager for the specified application
47) What are the different types of Essbase cache?
Answer
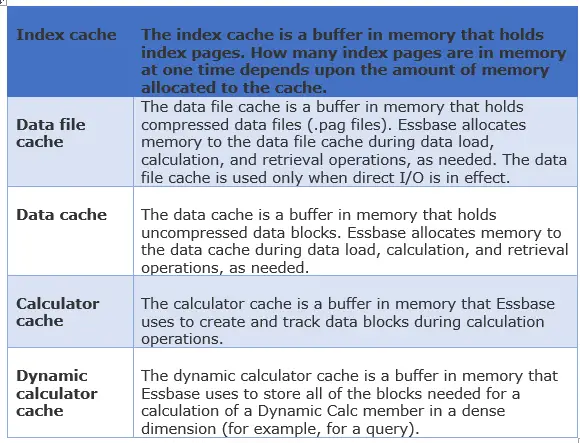
48) I have write access to one dimension, for other dimensions I have read access, is it possible to load data into dimensions?
49) what is the difference between shift and relative functions and where you use them?
50) what is a relative function?
51) In what case we can define generation 1 to a field in the generation build method?
Answer
We cannot define that as Generation 1 is not valid.
52) Suppose we have assigned Generation 2 and Generation 4 as of now and think of adding Generation 3 later sometime. Can we build the dimension?
Answer
No. If Gen 2 and Gen 4 exist, we must assign Gen 3.
53) Can we create more than 2 dimensions using only one build rule file?
Answer
Yes, we can do that but it is recommended to use separate rule files for each dimension.
54) Can we have multiple meta outlines based on one OLAP model in Integration services?
Answer Yes
55) Can we have a meta outline based on two different OLAP models?
Answer No.
56) What is the data block and index file in the BSO database?
Answer The data block is the structure that is comprised of the dimensions tagged as dense in the Essbase outline (.otl file). The block is defined by the intersections of all dense dimension member intersections. When data blocks and index entries are persisted to disk, the data blocks are compressed and stored within ESS.PAG files and index entries are stored within ESS.IND files.
57) Can we create UDAs and apply them to Dense as well as Sparse dimensions?
Answer Yes
58) What is a block locking system?
Answer
Analytic services (or Essbase Services) lock the block and all other blocks that contain the Childs of that block while calculating this block is the block locking system.
59) What are attributes?
Answer A classification of a member in a dimension. You can select and group members based on their associated attributes. You can also specify an attribute when you perform calculations and use calculation functions. Eg: The database in Sample Basic which has product dimensions has some attributes like size, package type, and flavour. We can add these attributes to the dimensions where we can retrieve the data like for example to retrieve “coke with 8 Oz with bottles”, this is useful for generating reports.
60) Why do objects get locked and when does this happen?
Answer Objects get locked to prevent users from making simultaneous and conflicting changes to Essbase database objects. By default, whenever an object is accessed through the Administrative services console or Excel spreadsheet add-in, it gets locked.
61) When does Fragmentation occur?
Answer Fragmentation is likely to occur with the following:
- Read/write databases that users are constantly updating with data
- Databases that execute calculations around the clock
- Databases that frequently update and recalculate dense members
- Data loads that are poorly designed
- Databases that contain a significant number of Dynamic Calc and Store members
- Databases that use an isolation level of uncommitted access with a commit block set to zero
62) How can you measure fragmentation?
Answer You can measure fragmentation using the average clustering ratio or average fragmentation Quotient.
Using the average fragmentation quotient
Any quotient above the high end of the range indicates that reducing fragmentation may help performance
Small (up to 200 MB) 60% or higher
Medium (up to 2 GB) 40% or higher
Large (greater than 2 GB) 30% or higher
Using the average clustering ratio:
The average clustering ratio database statistic indicates the fragmentation level of the data (.pag) files. The maximum value, 1, indicates no fragmentation.
63) How do you can prevent and remove fragmentation?
Answer
You can prevent and remove fragmentation:
- To prevent fragmentation, optimize data loads by sorting load records based on sparse dimension members. For a comprehensive discussion of optimizing data load by grouping sparse members.
- To remove fragmentation, perform an export of the database, delete all data in the database with CLEARDATA, and reload the export file.
- To remove fragmentation, force a dense restructure of the database.
64) What is database restructuring?
Answer
When you change the Essbase database outline to capture new product lines, provide information on new scenarios, reflect new time periods, etc. Some changes to a database outline affect the data storage arrangement, forcing Essbase to restructure the database.
65) What are the types of database restructuring?
Answer
The two ways by which a database restructure is triggered:
Implicit Restructures
Dense restructure
Sparse restructure
Outline-only restructure
Explicit Restructures
66) What are the conditions affecting Database restructuring?
Intelligent Calculation, name changes, and formula changes affect database restructuring:
- If you use Intelligent Calculation in the database, all restructured blocks are marked as dirty whenever data blocks are restructured. Marking the blocks as dirty forces the next default Intelligent Calculation to be a full calculation.
- If you change a name or a formula, Essbase does not mark the affected blocks as dirty. Therefore, you must use a method other than full calculation to recalculate the member or the database.
67) What are the files used during Restructuring?
Answer
When Essbase restructures both the data blocks and the index, it uses the files described
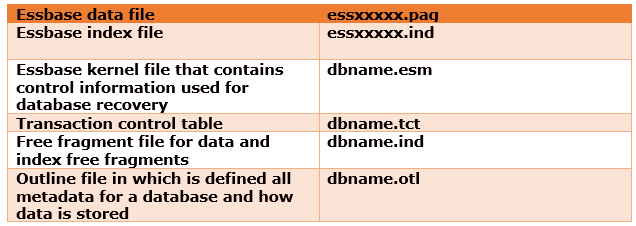
68) What are the actions that improve performance for restructuring?
Answer
There are a number of things you can do to improve performance related to database restructuring:
a) If you change a dimension frequently, make it sparse. ·
b) Use incremental restructuring to control when Essbase performs a required database restructuring. ·
c) Select options when you save a modified outline that reduces the amount of restructuring required.
69) Why do objects get locked and when does this happen?
Answer Objects get locked to prevent users from making simultaneous and conflicting changes to Essbase database objects. By default, whenever an object is accessed through the Administrative services console or Excel spreadsheet add-in, it gets locked.
70) I have created an application with one database in Essbase at the test environment and now need to copy the entire application with all security permissions to the production server which is not connected to the test server. How can I do that?
Answer: You can achieve this using a migration wizard to migrate an application to a text file which you can take physically to the production server.
71) When I migrated the application to the production server I did not see any data in the Essbase database. What has gone wrong and how to correct this?
Answer Nothing has gone wrong. Migration utility does not migrate the actual data. If you want to copy the exact data from the test machine, get it exported using export utility and import it on a production machine.
72) How can we backup an aggregate storage database?
Answer
a) shut down the application
b) copy the application directory ARBORPATH/app/appname.c) startup the application
73) How does Essbase recover from a database crash?
Answer After a database crash or server interruption, Essbase automatically recovers a database after rolling back the transactions that were active at that time.
74) How can you make a Max L script run at a specified time?
Answer MaxL scripts can be called from a BAT file which is used for scheduling.
75) A customer wants to run two instances of an Essbase server on the same machine to have both test env and Development env on the same server. Can he do that?
Answer
Yes. We can have multiple instances of an Essbase server on a single machine and there will be different sets of Windows services for all these instances
76) How to make the Essbase application read-write and read-only in case backup fails in that stage
Answer
Archive mode (Essbase application in read-only mode) By using of below command we can achieve that
alter database dbname begin archive
Essbase application read-write mode we can achieve that by using of below command
alter database dbname end archive
77) How can we back up a block storage database?
Answer
a) put the application in read-only mode
b) Take an archive of the whole application which contains all the files.
c) put the application back in read-write mode
78) What is dense restructuring?
Answer
If a member of a dense dimension is moved, deleted, or added, Essbase restructures the blocks in the data files and creates new data files. When Essbase restructures the data blocks, it regenerates the index automatically so that index entries point to the new data blocks. Empty blocks are not removed. Essbase marks all restructured blocks as dirty, so, after a dense restructure you must recalculate the database. Dense restructuring, the most time-consuming of the restructures, can take a long time to complete for large databases.
79) What is sparse restructuring?
Answer
If a member of a sparse dimension is moved, deleted, or added, Essbase restructures the index and creates new index files. Restructuring the index is relatively fast; the time required depends on the index size.
80) What is an Outline-only restructure
Answer
If a change affects only the database outline, Essbase does not restructure the index or data files. Member name changes, creation of aliases, and dynamic calculation formula changes are examples of changes that affect only the database outline.
81) How does Essbase perform Sparse restructuring?
Answer
When Essbase does a sparse restructure (restructures only the index), it uses the following files:
essxxxxx.ind
dbname.otl
dbname.esm
To perform a sparse restructure, Essbase does the following:
1 Renames the dbname.esm file to dbname.esr.
2 Renames the essxxxxx.ind files to essxxxxx.inm.
82) What is intelligent calc? Why should I care?
Answer
When you perform a full database calculation, Essbase marks which blocks have been calculated. If you then load a subset of data, you can calculate only the changed data blocks and their ancestors. This selective calculation process is intelligent calculation.
By default, the intelligent calculation is turned on. You can change the default setting in the essbase.cfg file or on a script-by-script basis with the SETUPDATECALC OFF command.
The intelligent calculation is based on data-block marking, when the intelligent calculation is active, during the normal processes, within the index file, blocks are marked clean or dirty.
Clean Blocks—Blocks that don’t require the calculation
Dirty Blocks — Blocks that require calculation.
When the intelligent calculation is active, during calculation, Essbase looks for only dirty blocks.
83) How to optimize the data loads in the BSO cube?
Answer
BSO load process is quite a complex process. Following action items can speed the data load in BSO
a) Positioning Data in the Same Order as the Outline
b) Loading from Essbase Server
c) Managing Parallel Data Load Processing
d) Grouping Sparse Member Combinations
e) Making the Data Source as Small as Possible
84) Explain the working of each of the tablespace in the ASO cube.
Answer
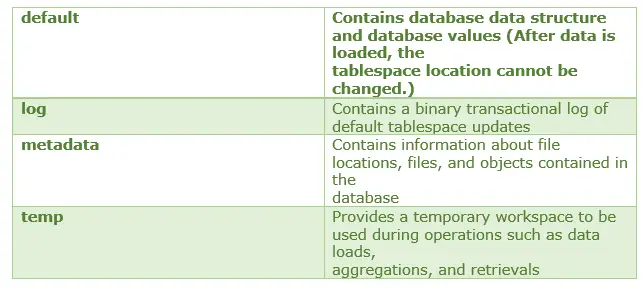
85) What is the use of OPMN in Essbase?
Answer
Oracle Process Manager and Notification Server (Oracle Process Manager and Notification
Server) enables you to monitor and control the Essbase Agent process. You add Essbase Agent information to the opmn.xml file to enable OPMN to start, stop, and restart the agent using the OPMN command-line interface. OPMN can automatically restart the Essbase Agent when it becomes unresponsive, terminates unexpectedly, or becomes unreachable as determined by ping and notification operations
86) What is active-active clustering?
Answer
Active-active Essbase clusters are the cluster of Essbase.it supports high availability and load balancing. So, all the Essbase nodes are serving the request. An active-active Essbase cluster supports read-only operations on the databases and should be used only for reporting. Because active-active Essbase clusters do not support data write-back or outline modification, and they do not manage database replication tasks such as synchronizing the changes in one database across all databases in the cluster, they do not support Planning.
87) what is active-passive clustering?
Answer
An active-passive Essbase cluster consists of two Essbase instances, one on each node that shares common storage for configuration and data. Storage is shared across two computers which removes the need for the administrator to synchronize storage, as well as the constraint of read-only support (as is the case with Essbase active-active clusters in Provider Services). Essbase uses database tables to ensure that only one agent and its associated servers are active to avoid data corruption on writes. During installation and configuration, a table is created to hold information on configuration and application data existing in the cluster.
Active-passive Essbase clusters do not use any file-system locking (that is, essbase.lck files).
Some of the features
- a) Active-passive Essbase clusters support failover with write-back to databases.
- b) Active-passive Essbase clusters do not support load-balancing.
- c) An active-passive Essbase cluster can contain only two Essbase servers.
88) What is a split-brain problem in Essbase clusters?
Answer
A split-brain situation can occur when both instances in an active-passive clustered environment think they are “active” and are unaware of each other, which violates the basic premise of active-passive clustering (One node being active). Situations where split-brain can occur include network outages or partitions. Such a situation can result in corruption
89) How Essbase resolve the split-brain problem?
Answer
Essbase failover uses a leasing mechanism to solve the problem of split-brain
90) How Leasing mechanism works in Essbase?
Answer
An Essbase process acquires a lease on a specified shared resource or set of resources upon startup; it renews the lease periodically and surrenders the lease upon termination.
This lease establishes the process as the primary service provider and grants the right to update the specified set of shared resources, service client requests, and spawn processes.
Essbase servers can acquire leases if and only if its authorizing agent has a current lease.
91) How Leases are Implemented internally in Essbase?
Answer
Essbase failover implements a leasing mechanism using a centralized relational database to store, update, and retrieve information about the following:
- a) Shared resources
- b) Lease ownership
- c) Lease validity
92) How to stop/start Essbase server?
Answer
We start/stop the Essbase server using OPMN (Oracle Process Manager). Upon Essbase installation, it registers Essbase Server for OPMN. OPMN manages the Essbase Agent, which manages the Essbase Server. Essbase Server start and stop scripts redirect to OPMN
93) What are these executable Essbase.exe and esssvr.exe in Windows?
Answer
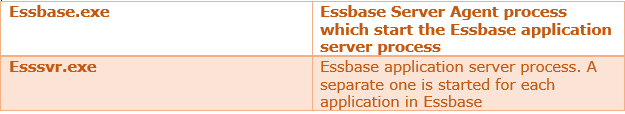
94) What does the Essbase security file Contains? Where is, it located?
Answer
Essbase.sec is an important file for Essbase server functioning.
Essbase is EPM System security mode (Shared services)
Calculation script access
Users and Groups details
Application and Database access type
Application and database properties, including substitution variables and DISKVOLUMES settings
Filters access
Locked objects
Substitution Variables
Passwords are not stored in Security files as they are stored in shared services.
Essbase is in native security mode
Stores all information about users, groups, passwords, permissions, filters, applications, databases, and corresponding directories
Essbase security file is located in Arborpath/bin directory
\Oracle\Middleware\user_projects\epmsystem1\EssbaseServer\essbaseserver1\bin
95) How to restore the Essbase security file after corruption?
Answer
- a) Stop the Essbase services
- b) Copy the essbase_timestamped.bak file from the same arborpath/bin folder and rename it to essbase.sec
- c) Restart the essbase services
Note: Each time the Essbase server restarts, a backup copy of the security file is created and named essbase.bak file
96) What is maxl?
Answer
Maxl is a multidimensional database access language that is part of Essbase – Servers provide a flexible way to automate Essbase administration and maintenance tasks
97) What is ARBORPATH?
Answer
ARBORPATH is an environment variable that defines the home directory for the Essbase – Server. It contains two main directories
| app | The app directory location where Essbase application files (as they are created) and sample applications and databases (provided with Essbase) are stored. |
| Bin | The bin directory location where Essbase configuration setting (essbase.cfg) and security (essbase.sec and essbase_timestamp.bak) files (as they are created) are stored. |
98) What is Essbase exception logs (.xcp)?
Answer
If an Essbase Server, an application, or a database shuts down abnormally and cannot restart, Essbase Server generates an exception log to help troubleshoot the problem. The location of the exception log depends on which component shut down abnormally and the amount of information that the Essbase Server had available at the time
99) What is a transaction in Essbase?
Answer
When a database is in read/write mode, Essbase considers every update request to the server (such as a data load, a calculation, or a statement in a calculation script) as a transaction. Essbase tracks information about transactions in a transaction control file (dbname. tct). The transaction control file contains an entry for each transaction and tracks the current state of each transaction (Active, Committed, or Aborted).
100) How to restore the Essbase application?
Answer
We need to replace the files on disk with the corresponding files from backup to restore a database, The application should be stopped unless you are restoring from an export file. In that case, ensure the application is not accepting client connections.
Also Reads
Windows grep equivalent
Senior Oracle DBA interview Questions