We have heard a lot about iaas paas saas in cloud computing terms. IaaS stands for Infrastructure as service, PaaS stands for Platforms as a service and SaaS stands software as a service

Let’s take a look at the key difference between them and examples of them
(1) IAAS
This is known as Infrastructure as a Service. Here the cloud provider gives the Physical infrastructure (network, storage, Computing power. Virtual machines) as a service that can be accessed over the internet. You can use that to install your software, application deployment, etc. The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure but has control over operating systems, storage, and deployed applications; and possibly limited control of select networking components
Users of IaaS can outsource and build a “virtual data center” in the cloud and have access to many of the same technologies and resource capabilities of a traditional data center without having to invest in capacity planning or the physical maintenance and management of it.
IaaS users are responsible for managing applications, data, runtime, middleware, and OSes.
IaaS Providers like Oracle still manage virtualization, servers, hard drives, storage, and networking.
The advantage here is that users can install any required platform on top of IaaS.
Example
AWS Elastic Compute Service or EC2 is IaaS(Infrastructure as a Service). This is because Amazon takes the responsibility of networking, storage, server, and virtualization and the user is responsible for managing the Operating System, middleware, runtime, data, and application.
AWS Simple storage server is also an example IaaS
Oracle Elastic Compute service is also an example of IaaS(Infrastructure as a Service)
Microsoft Azure Virtual Machine is IaaS
(2) PAAS
This is known as Platform as a Service. Here cloud providers deliver a computing platform, typically including operating system, programming-language execution environment, database, and web server. Application developers can develop and run their software solutions on a cloud platform without the cost and complexity of buying and managing the underlying hardware and software layers. The consumer does not manage or control the underlying cloud infrastructure including network, servers, operating systems, or storage, but has control over the deployed applications and possibly configuration settings for the application-hosting environment.
PaaS basically help the developer to speed the development of the app, saving money and most important innovating their applications and business instead of setting up configurations and managing things like servers and databases
Applications using PaaS inherit cloud characteristics such as scalability, high availability, multi-tenancy, SaaS enablement, and more
Example
AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Windows Azure, Heroku, Force.com, Google App Engine, Apache Stratos.
Oracle Database cloud server and Oracle Exadata cloud database is a classic example of PAAS(Platform as a service)
Microsoft sql Azure is a great example of PaaS
(3) SAAS
This is known as Software as a Service. Here cloud providers install and operate application software in the cloud and cloud users access the software from cloud clients. SaaS is sometimes referred to as “on-demand software” and is usually priced on a pay-per-use basis or using a subscription fee. Cloud users do not manage the cloud infrastructure and platform where the application runs. the cloud provider manages the infrastructure and platform both.
Cloud providers develop, maintain the software. Users just used the service through the internet. The amount of configuration or set up at your end is minimal. Service Provider takes care of hardware, software updates, security, and patches
With this offering, complete offloading is done to the service provider. The organization just needs to access the software through the internet.
Also, there’s no need to invest in server capacity and software licenses. Simply adjust the subscription.
Some of the disadvantages of the SAAS model are
a) The customer has no control over the system processing its data.
b) There is no control over which customers use the software; the software is used by a large number of users.
c) Little or no control over the parameters of the software. Only minimal configuration changes are allowed
d) Little control over deployment, upgrade, and testing methodology (e.g. Dev, UAT, Live systems availability)
e) Currently only a limited number of software solutions are offered in the form of SaaS.
SaaS Example
Google Apps, Salesforce, Workday, Concur, Citrix GoToMeeting, Cisco WebEx, Microsoft 365, Oracle HCM Cloud, Oracle ERP cloud
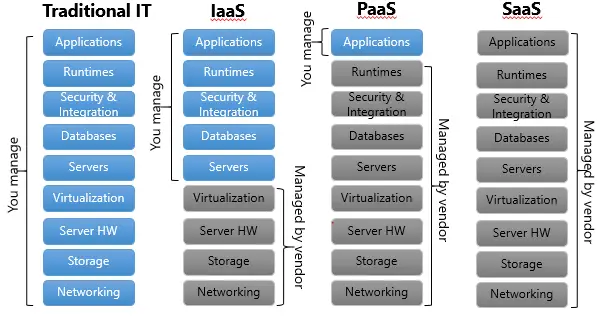
We can summarize the difference with the below image
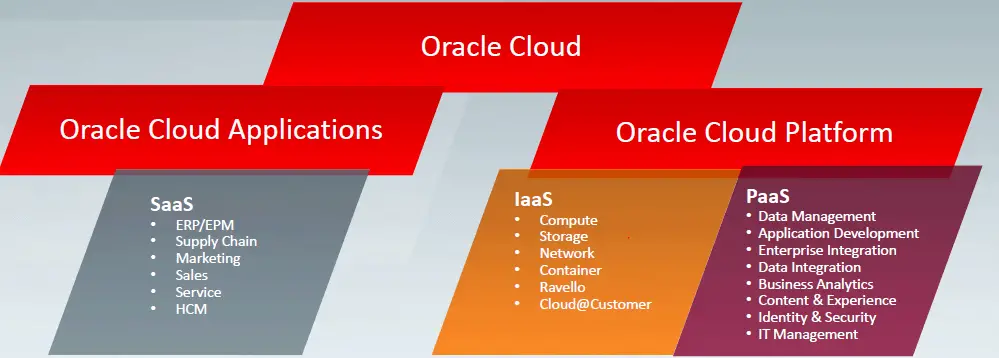
We can take Oracle Products as an example to differentiate between these models
Another example could be Microsoft Azure
IaaS: Virtual machine, network storage
Paas: Azure sql database, Window Azure OS, NAPA
SAAS: Office 365, Sharepoint, Intune
A video from Youtube to help you understand it
Related Articles
Linux Operating System and Distribution : Article about Linux Operation system, Kernel, Various distribution available in Market.Learn about Oracle Enterprise Linux
oracle cloud infrastructure : Oracle Infrastructure as a Service is called Oracle Cloud Infrastructure (OCI).It offers storage,compute, database, networking, edge services
what is cloud computing : Learn about what is cloud computing and how it can benefit organizationas Various cloud models, cloud vendors, cloud examples
oracle iaas: overview about various Oracle Cloud: Infrastructure-as-a-Service like Compute,storage,network services with various options
Virtualization : Virtualization is the process of creating multiple virtual machines /operating system from one physical hardware box with the help of a hypervisor
Recommended Courses
Cloud Computing Concepts : it Covers Fundamentals of Cloud Computing and types of cloud-like private, public, hybrid, IAAS, SAAS, PAAS, and cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud. One of must-have course for anybody starting with Cloud
Introduction to Cloud Computing on Amazon AWS for Beginners : Learn about Amazon Web services.Various offerings are available with it like EC2, EBS ,S3. A good course for anybody starting with AWS
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) Fundamentals for Beginners : Learn how to use GCP compute, storage, and networking services, Key services of Google Cloud Platform.A good course for anybody starting with GCP
Introduction to Cloud Security with Microsoft Azure : It covers Azure services, Azure PowerShell. A good course for anybody starting with Microsoft Azure