Lead function in oracle
LEAD Function in Oracle is a Analytic function which has the ability to compute an expression on the next rows (rows which are going to come after the current row) and return the value to the current row. The general syntax of LEAD is shown below:
LEAD (<expr>, <offset>, <default>) OVER (<analytic_clause>)
<expr> is the expression to compute from the leading row.
<offset> is the index of the leading row relative to the current row and its default value is 1
<default> is the value to return if the <offset> points to a row outside the partition range.If you skip default, then the function will return NULL.
Lets take an example to get the feel of it. First lets prepare the example data
CREATE TABLE "DEPT"
( "DEPTNO" NUMBER(2,0),
"DNAME" VARCHAR2(14),
"LOC" VARCHAR2(13),
CONSTRAINT "PK_DEPT" PRIMARY KEY ("DEPTNO")
)
CREATE TABLE "EMP"
( "EMPNO" NUMBER(4,0),
"ENAME" VARCHAR2(10),
"JOB" VARCHAR2(9),
"MGR" NUMBER(4,0),
"HIREDATE" DATE,
"SAL" NUMBER(7,2),
"COMM" NUMBER(7,2),
"DEPTNO" NUMBER(2,0),
CONSTRAINT "PK_EMP" PRIMARY KEY ("EMPNO"),
CONSTRAINT "FK_DEPTNO" FOREIGN KEY ("DEPTNO")
REFERENCES "DEPT" ("DEPTNO") ENABLE
);
SQL> desc emp
Name Null? Type
---- ---- -----
EMPNO NOT NULL NUMBER(4)
ENAME VARCHAR2(10)
JOB VARCHAR2(9)
MGR NUMBER(4)
HIREDATE DATE
SAL NUMBER(7,2)
COMM NUMBER(7,2)
DEPTNO NUMBER(2)
SQL> desc dept
Name Null? Type
---- ----- ----
DEPTNO NOT NULL NUMBER(2)
DNAME VARCHAR2(14)
LOC VARCHAR2(13)
insert into DEPT values(10, 'ACCOUNTING', 'NEW YORK');
insert into dept values(20, 'RESEARCH', 'DALLAS');
insert into dept values(30, 'RESEARCH', 'DELHI');
insert into dept values(40, 'RESEARCH', 'MUMBAI');
commit;
insert into emp values( 7839, 'Clark', 'MANAGER', 7839, to_date('9-6-2008','dd-mm-yyyy'), 28573, null, 10 );
insert into emp values( 7782, 'Clara', 'MANAGER', 7839, to_date('9-6-2008','dd-mm-yyyy'), 0, null, 10 );
insert into emp values( 7934, 'Blake', 'MANAGER', 7839, to_date('1-5-2007','dd-mm-yyyy'), 0, null, 10 );
insert into emp values( 7788, 'Scott', 'ANALYST', 7788, to_date('9-6-2012','dd-mm-yyyy'), 30000, null, 20 );
insert into emp values( 7902, 'Bill', 'ANALYST', 7832, to_date('9-6-2012','dd-mm-yyyy'), 30000, null, 20 );
insert into emp values( 7876, 'TPM', 'ANALYST', 7566, to_date('9-6-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 11000, null, 20 );
insert into emp values( 7369, 'TPM1', 'ANALYST', 7566, to_date('9-6-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 8000, null, 20 );
insert into emp values( 7698, 'A1', 'ANALYST', 7788, to_date('9-6-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 28500, null, 30 );
insert into emp values( 7499, 'A2', 'ANALYST', 7698, to_date('9-7-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 16000, null, 30 );
insert into emp values( 7844, 'A3', 'ANALYST', 7698, to_date('9-7-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 15000, null, 30 );
insert into emp values( 7654, 'A4', 'ANALYST', 7698, to_date('9-7-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 12500, null, 30 );
insert into emp values( 7521, 'A5', 'ANALYST', 7698, to_date('9-7-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 12500, null, 30 );
insert into emp values( 7900, 'A6', 'ANALYST', 77698, to_date('9-7-2017','dd-mm-yyyy'), 0, null, 30 );
commit;
Now we can use the Lead Function in Oracle as per below query
SQL> SELECT deptno, empno, sal,LEAD(sal, 1, 0) OVER ( partition by deptno ORDER BY sal DESC NULLS LAST) NEXT_LOWER_SAL FROM emp;
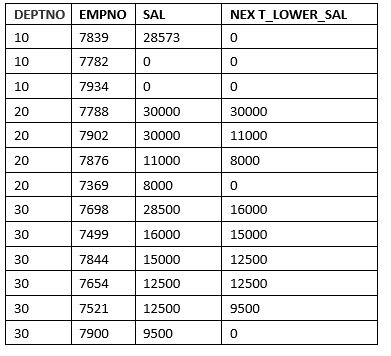
Taking Different Default Value
SELECT deptno, empno, sal,LEAD(sal, 1,100) OVER ( partition by deptno ORDER BY sal DESC NULLS LAST) NEXT_LOWER_SAL FROM emp;
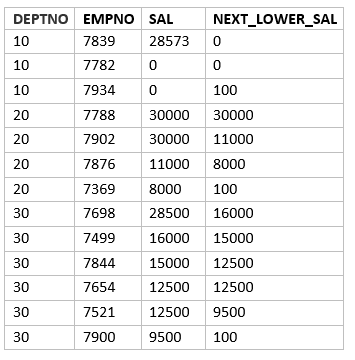
If dont give any values for default,then it gives null where there is no value. This is shown in below query
SELECT deptno, empno, sal,LEAD(sal) OVER ( partition by deptno ORDER BY sal DESC NULLS LAST) NEXT_LOWER_SAL FROM emp;
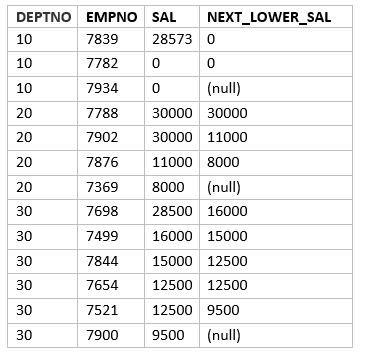
LAG function in Oracle
Similarly LAG provides the technique to compute on previous rows and return the value to the current row
LAG (<expr>, <offset>, <default>) OVER (<analytic_clause>)
<expr> is the expression to compute from the previous row.
<offset> is the index of the previous row relative to the current row and its default value is 1
<default> is the value to return if the <offset> points to a row outside the partition range.If you skip default, then the function will return NULL.
Taking the same data set as earliar
SQL> SELECT deptno, empno, sal,LAG(sal, 1,0) OVER ( partition by deptno ORDER BY sal DESC NULLS LAST) LAST_HIGH_SAL FROM emp;
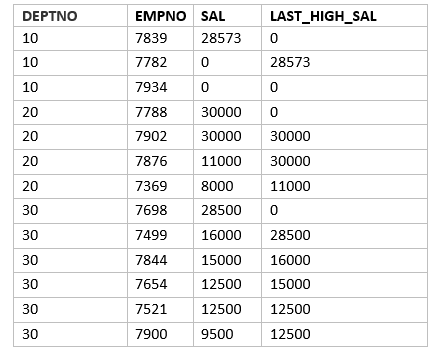
If dont give any values for default,then it gives null where there is no value. This is shown in below query
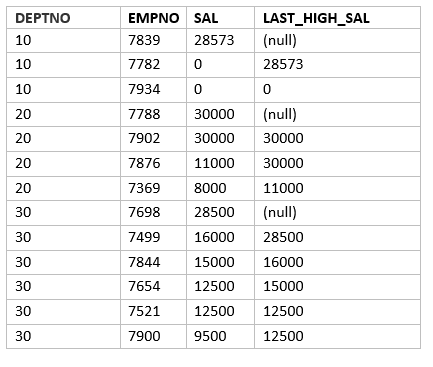
SQL> SELECT deptno, empno, sal,LAG(sal) OVER ( partition by deptno ORDER BY sal DESC NULLS LAST) LAST_HIGH_SAL FROM emp;
I hope you like this article on Lead and Lag function in Oracle.These can be very useful in many areas. Please do provide the feedback
Related Articles
Oracle Interview questions
Analytic functions in oracle
RANK function in Oracle
Dense_Rank function in Oracle
NULLIF function in Oracle
https://docs.oracle.com/en/database/oracle/oracle-database/12.2/sqlrf/LEAD.html#GUID-0A0481F1-E98F-4535-A739-FCCA8D1B5B77
Very nice article on analytical functions
thanks Madhu