SubQueries in Oracle
(1) A Subquery or Nested query is a query within another SQL query and embedded within the WHERE clause. A subquery is a query within a query
(2) A subquery is used to return data that will be used in the main query as a condition to further restrict the data to be retrieved.
(3) Subqueries answer the queries that have multiple parts. The parent query answers a part and the sub query answers other part
(4)Subqueries can be used with the SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE statements along with the operators like =, <, >, >=, <=, IN, BETWEEN etc.
(5)Using subqueries in a FROM clause is known as an inline view.
(6) Using subqueries in the WHERE clause is called a nested subquery. Up to 255 nested queries are allowed.
Some Guidelines for Oracle SubQueries
(1) We need to put sub queries in parenthesis always
(2) We need to place subqueries on the right side of the comparison operator
(3) Use single row operator with single row subqueries and multiple row operator with multiple row subqueries
General Syntax
SELECT col1, col2 FROM table1 WHERE col1 OPERATOR (SELECT col1 FROM table2 [WHERE])
Single Row Subquery
It returns only one row of results and uses a single row operator (most common is the equal operator (=)). The other operators are > ,< ,>= ,=<
Single row subqueries can select data from the same table or from another table
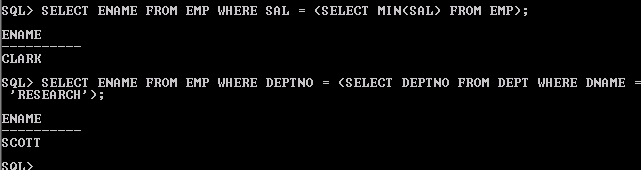
SELECT ENAME FROM EMP WHERE SAL = (SELECT MIN(SAL) FROM EMP);SELECT ENAME FROM EMP WHERE DEPTNO = (SELECT DEPTNO FROM DEPT WHERE DNAME = 'RESEARCH');
Multiple Row Subquery
It returns several rows of results from the subquery, uses the IN operator. In the previous query, if there was more than one research department, the query would have failed. Example of returning more than one row in the subquery
The other operator which are used is any and all
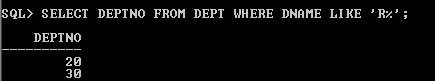
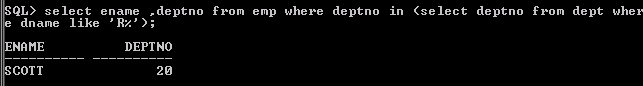
SELECT ENAME, DEPTNO FROM EMP WHERE DEPTNO IN (SELECT DEPTNO FROM DEPT WHERE DNAME LIKE 'R%');
Correlated Subquery
A correlated subquery is a subquery that relies on columns from the parent query. A correlated subquery is evaluated for each row processed by the parent query. The parent statement can be a SELECT, UPDATE or DELETE.
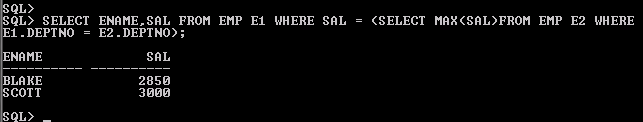
SELECT ENAME,SAL FROM EMP E1 WHERE SAL = (SELECT MAX(SAL) FROM EMP E2 WHERE E1.DEPTNO = E2.DEPTNO);
Based on the same data of emp and dept ,here is the result
Scalar Subqueries
It returns exactly one value from one row, used most often in the VALUES clause of an INSERT statement, in and ORDER BY or WHERE clause and in a SELECT clause:
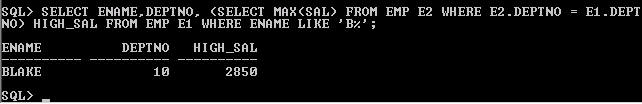
SELECT ENAME, DEPTNO, (SELECT MAX(SAL) FROM EMP E2 WHERE E2.DEPTNO = E1.DEPTNO) HIGH_SAL FROM EMP E1 WHERE ENAME LIKE 'B%';
The sub query executes once for each execution of the master query. A single-row subquery can only be used with single-row operators
Multiple-Column Subqueries
The query can have more than one column in the SELECT clause of a subquery or in UPDATE statements
SELECT CITY,CITY_CODE,CITY_DESCRIPTION FROM LOCATIONS WHERE (LOCATION_ID, COUNTRY_ID) IN (SELECT LOCATION_ID, COUNTRY_ID FROM LOCATIONS WHERE STATE_PROVINCE = 'NEWYORK');
Subqueries in other DML Statements
Subqueries can be used in UPDATE, DELETE and INSERT statements
Update Statement UPDATE EMP SET SALARY = (SELECT SALARY FROM EMP WHERE EMPLOYEE_ID = 112408) WHERE EMPLOYEE_ID = 193711; Insert Statement INSERT INTO DEPT (DEPT_ID, DEPT_NAME) VALUES ((SELECT MAX(DEPT_ID) FROM DEPT), 'NEW DEPT'); Delete Statement DELETE FROM CUSTOMERS WHERE AGE IN (SELECT AGE FROM CUST_BACK WHERE AGE > 40 );
Related Articles
how to write sql queries :What are Oracle Joins with examples (Sql joins), Different type of joins , Inner Join,Outer join,left outer join,right outer join,cross join with examples
Oracle Joins :What are Oracle Joins with examples (Sql joins), Different type of joins , Inner Join,Outer join,left outer join,right outer join,cross join with examples
Date functions in oracle :Check out this post for oracle date functions, oracle date difference in years,oracle date difference in days, oracle date difference in months.
JSON in oracle : Check out this post on how to use JSON in oracle,how to create table containing JSON data, how to extract,insert the JSON data in oracle
Oracle Sql tutorial : Listing of all the sql tutorial lessons which can be used to master sql and use in Oracle, data management and manipulation
https://livesql.oracle.com/apex/livesql/file/tutorial_GMLYIBY74FPBS888XO8F1R95I.html
Hi,
But a multiple-row subquery can have more than one column?
Thanks
Yes we can multiple column subquery with multiple rows
SELECT CITY,CITY_CODE,CITY_DESCRIPTION
FROM LOCATIONS
WHERE (LOCATION_ID, COUNTRY_ID)
IN (SELECT LOCATION_ID, COUNTRY_ID
FROM LOCATIONS
WHERE STATE_PROVINCE = ‘NEWYORK’);
Your example for scalar subquery looks like a correlated subquery. Scalar subquery caching won’t work on this because of the WHERE E2.DEPTNO = E1.DEPTNO and therefore I’d say the SQL engine doesn’t see this as a scalar subquery.