Why Multitenant Architecture introduced with 12c?
Many Oracle customers have large numbers of applications built on Oracle RDBMS. They do not use a significant percentage of the hardware on which they are deployed.Customers have instance and storage overhead preventing large numbers of databases from being placed on the same physical and storage server. They are not generally complex to require 100% of the attention of a full time administrator And they do require significant time to patch or upgrade all applications.
Oracle Multitenant Architecture is the answer to all these problems. It basically provides a cloud of Oracle database.
What is Multitenant Architecture?
Multiple tenants share same resources on a mutual benefit for different purposes at a very broad level. The same applies to Oracle Database where Multiple Databases share a single instance of resources aiming for different purposes on the same Server. This Oracle Database which is built on Multitenant foundation is called Container Database(CDB), and each container(tenant) residing inside is called Pluggable Database(PDB, Container).
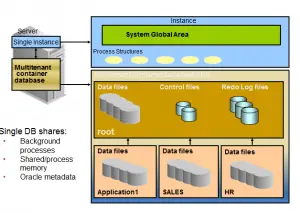
Features
(1) All the Pluggable database shares the same background process, Shared /process memory,Oracle metadata
(2) All the Pluggable database shares the redo log file,control files and undo tablespace. With 12.2 we have undo tablespace is not shared
(3) There are two types of containers in Multitenant Architecture
The root container
-The first container created at CDB creation
-Mandatory
-Oracle system-supplied common objects and metadata
-Oracle system-supplied common users and roles
Pluggable database containers (PDBs):
-A container for an application
-Tablespaces (permanent and temporary)
–Schemas / objects / privileges
–Created / cloned / unplugged / plugged
Particular seed PDB:
–PDB$SEED provides fast provisioning of a new PDB
(4) There is a Limit of 253 PDBs in a CDB including the seed
(5) There is a Limit of 1024 services in a CDB
(6) Every PDB has its own set of SYSTEM/SYSAUX/TEMP tablespaces, and also includes the Sample User data such as SCOTT etc..
(7) ENABLE_PLUGGABE_DATABASE initialization parameter specifies If a particular Database is CDB or Non-CDB
Benefits
(1) It operates multiple database in a centrally managed platform to lower costs .It basically consolidates all the databases.It means less instance overhead and less storage utilization. Till 11g,we have databases deployed across multiple Small Physical machines on various platforms. It could be waste of resources having a database on each machine dedicated rather keeping them all on a single powerful machine. 12c Multitenant architecture consolidates all Databases onto a Single powerful chip and a Single Oracle Instance
(2) It allows central management and database administration of multiple database. Backup and recover, patching ,upgrade becomes simpler
(3) It is supported with Oracle Dataguard and Oracle RAC,So Disaster recovery and High Availability can be achieved for multiple database at the same time
(4) It reduces the DBA resource costs
Container Database (CDB) and Pluggable Database (PDB) :- Oracle Database 12c Container database and Pluggable database
Oracle 12c New Features for developers: Useful features for Developer with Oracle 12c and above
Oracle 12c Database Installation on Linux :- Step by Step Oracle 12c Database Installation on Linux system
Very useful 10 new things in 12c database
How to Create the container database
How to create Pluggable database in 12c database
Further Reference
https://docs.oracle.com/database/121/CNCPT/cdbovrvw.htm