Here we will be discussing about Oracle PLSQL Block Structure and types, what is pl sql block in oracle, and what is pl sql block structure, how to write pl sql block
what is pl sql block
PL SQL is a block-structured language. Here we divided programs into logical blocks
PLSQL Block Structure
A plsql block is made in three sections Declare, executable and exception.
| DECLARE(Optional) – this section contains variables, constants, cursors, and user-defined exceptions. BEGIN(Mandatory) EXECUTABLE – this section contains any SQL statements. EXCEPTION (optional)- This section contains the error handlers.END(Mandatory); |
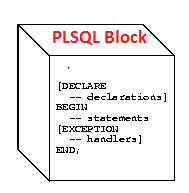
So Declare and exception sections are Optional.
plsql block example
DECLARE
l_number NUMBER;
BEGIN
l_number := 1;
Dbms_output.put_line(l_number);
Exception
When others then
Dbms_output.put_line(‘Exception occurred’);
END;
/
DECLARE
l_ret boolean;
l_user_id number;
BEGIN
select user_id
into l_user_id
from fnd_user
where user_name = '&USER_NAME';
l_ret := fnd_profile.DELETE(X_NAME => 'FND_INIT_SQL',
X_LEVEL_NAME => 'USER',
X_LEVEL_VALUE => l_user_id);
commit;
dbms_output.put_line('Profile has erased successfully');
EXCEPTION
when others then
dbms_output.put_line('Failed to erase the profile: '||sqlerrm);
END;
/
DECLARE
v_user_name VARCHAR2 (100) := upper('TEST');
v_description VARCHAR2 (100) := 'TEST';
BEGIN
fnd_user_pkg.createuser
(x_user_name => v_user_name,
x_owner => NULL,
x_unencrypted_password => 'welcome1233TEST',
x_session_number => 0,
x_start_date => SYSDATE,
x_end_date => NULL,
x_last_logon_date => NULL,
x_description => v_description,
x_password_date => NULL,
x_password_accesses_left => NULL,
x_password_lifespan_accesses => NULL,
x_password_lifespan_days => NULL,
x_employee_id => NULL,
x_email_address => NULL,
x_fax => NULL,
x_customer_id => NULL,
x_supplier_id => NULL,
x_user_guid => NULL,
x_change_source => NULL
);
COMMIT;
END;
/
Important points to Note down
(1) All the variables and constants are defined in declare section
(2) Place a semicolon; at the end of sql statement or plsql control statement
(3) In PL/SQL all the errors are handled in the Exception block.
(4) Begin and End is mandatory statements indicating begin and end of the PL/SQL Block.
(5) Variables and Constants must be declared first before they can be used.
(6) Values can be assigned to variables directly using the “:=” assignment operator, by way of a SELECT … INTO statement or When used as OUT or IN OUT parameter from a procedure.
(7) Section keywords Declare, Begin, and exception are not followed by semicolons
(8) End and all other plsql statement requires a semicolon to terminate the statement
PLSQL Block Types
Anonymous: Anonymous Blocks are unnamed blocks. They are declared at the point in the application where they need to be executed
DECLARE l_number NUMBER; BEGIN l_number := 1; Dbms_output.put_line(l_number); Exception When others then Dbms_output.put_line(‘Exception occurred’); END; /
Function: These are named PLSQL blocks that can accept the parameter and compute some function and return it. It can be stored in an Oracle server or application
Syntax FUNCTION name [(parameter[, parameter, …])] RETURN datatype IS [local declarations] BEGIN executable statements [EXCEPTION exception handlers] END [name]; Example Create or replace function FUNC return number As l_number NUMBER; BEGIN Select count(*) into l_number from emp; return(l_number) END; /
Procedure: These are named PLSQL blocks that can accept parameters and process some information and may or may return values. It can be stored in an Oracle server or application
Syntax PROCEDURE name [(parameter[, parameter, …])] IS [local declarations] BEGIN executable statements [EXCEPTION exception handlers] END [name]; Example Create or replace procedure remove_emp (emp_id number) As BEGIN Delete from emp where employee_id=emp_id; END; /
Difference Between Function and Procedure
| Function | Procedure |
| Function must return a value | Procedure need not |
| Syntax | Syntax |
| FUNCTION name (argument list …..) Return datatype is | PROCEDURE name (parameter list…..) |
| local variable declarations | is |
| Begin | local variable declarations |
| executable statements | BEGIN |
| Exception | Executable statements. |
| execution handlers | Exception. |
| End; | exception handlers |
| end; | |
| Function can be used in SQL with some restriction | Procedure cannot be called directly from SQL. |
Oracle PLSQL Block Syntax and Guidelines/how to write pl sql block
1) Character and date literals must be enclosed in single quotation marks
2) Place multiple line comments between /* and */
3) Most of the sql functions can be used in PLSQL. We have char, date, and number functions available in PLSQL just like SQL
4) group by function are not available in PLSQL. It can be only used in the sql statement in the PLSQL
5) We should use proper indentation to make the code readable
6) It is recommended to write the DML statement in Upper case, PLSQL Keywords, and Datatypes in Upper case and Put identifiers and parameters in lower case for better readability and maintenance
Summary
- A plsql block is made in three sections Declare, executable and exception.
- plsql block can be an anonymous block or function or Procedure
Related links
Oracle PLSQL Variable: Check out this post on Oracle PLSQL Variable, how to declare variable in stored procedure oracle
Oracle PLSQL records: Check out this article on the working of oracle plsql records. Also, find out the various ways to define it and assign value to it
PLSQL Tables: Check out this post for a detailed description of PLSQL Tables.How to manipulate it and work on it in Oracle PLSQL block and benefits
What is cursor in oracle : Check out this post to get a great overview of What is cursor in oracle.Details about Cursor parameter, cursor loop, cursor for an update
Oracle PLSQL documentation
Oracle PlSQL interview question
