What is Sequence in Oracle?
- Oracle Sequence is a user-created object which can be shared by multiple users to generate unique integers
- The most general use of sequences would be to generate a primary key column in the table.
- The sequence is generated by Oracle’s internal routine so we don’t need to worry about it. It will save time as developers don’t need to generate the sequence-producing routine
- A sequential number generator can be configured to increase or decrease
- It exists only in the data dictionary and can be limited or repeatable (cycle).
- We need to have create sequence privilege to create the sequence
Creating a sequence is done using the
CREATE SEQUENCE [START WITH] [INCREMENT BY] [NO/MINVALUE] [NO/MAXVALUE] [NO/CYCLE] [NO/CACHE];
Description of each value

Examples
create sequence test_tech start with 1
increment by 1
maxvalue 10000
cycle
cache 20;
Or
create sequence test_tech1
start with 1
increment by 1
maxvalue 4500000
cycle
nocache;
How to use sequences
To use sequence simply use the CURRVAL and NEXTVAL pseudo column
NEXTVAL pseudo column
It is used to generate the successive sequence number of the specified sequence
CURRVAL pseudo column
It holds the sequence which the user just generated
SELECT TEST_TECH.NEXTVAL FROM DUAL;
SELECT TEST_TECH.CURRVAL FROM DUAL;
SELECT TEST_TECH.NEXTVAL FROM DUAL;
How to Modify the Sequences
We can modify the sequences using an alter sequence.
SQL> ALTER SEQUENCE tech_test1 INCREMENT BY 50;
- The changes impact only the future use of the sequence.
- You must be the owner or have alter privilege on that sequence
- We cannot change “start with” option. For this sequence needs to be dropped and recreated
- Sequence changes are also validated
How to drop the sequence
Dropping a view is done using the DROP sequence command.
Drop sequence test_tech ;
Dictionary Views for seeing the sequence data
sequence details can be queried from the dictionary by querying either USER_SEQUENCES, ALL_ SEQUENCES, or DBA_ SEQUENCES. There are three categories of views
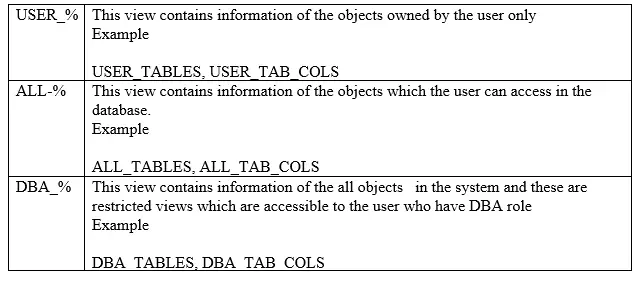
| DBA_% views about sequences | ALL_% views about sequences | USER_% views about sequences | |
| View about sequences information | dba_sequences | all_ sequences | user_ sequences |
To list all sequences owned by the current use
select sequence_name from user_sequences;
To list all sequences in a database:
Select owner, sequence_name from dba_sequences;
To list sequences accessible to the current user:
select sequence_name from all_sequences
How to determine the all information about the sequence?
select sequence_name,min_value,max_value,increment_by,last_number
FROM DBA_SEQUENCES
where OWNER = '<owner_name>'
and sequence_NAME = '<sequence_name>';
How to retrieve the current value of an oracle sequence without incrementing it
The last_number column displays the next available sequence number if no cache is specified
SELECT last_number FROM user_sequences WHERE sequence_name = '<sequence_name>';
How to extract the sequence definition (DDL statements) from an Oracle database without having to go through a stack of dictionary views
Syntax:
SQL> set long 1000
SQL> set pagesize 0select DBMS_METADATA.GET_DDL('SEQUENCE','<sequence_name>') from DUAL;
How to set the LAST VALUE value in an Oracle Sequence
ALTER SEQUENCE tech_seq_name INCREMENT BY 250;
SELECT tech_seq_name.nextval FROM dual;
ALTER SEQUENCE tech_seq_name INCREMENT BY 1;
How to Reset a Sequence in Oracle
There are many ways.
a) We can drop and recreate the sequence. But this invalidates all dependent objects (triggers/stored procedures etc.)
b) We can reset by these simple steps
Step 1:Find the latest value of the sequence Select tech_seq_name.nextval FROM dual; Step 2: alter the sequence with increment of the negative value of the latest value ALTER SEQUENCE tech_seq_name INCREMENT BY -< latest value> minvalue 0; Step 3 Do nextval to set it back to zero SELECT tech_seq_name.nextval FROM dual; Step 4: Change increment back to 1 ALTER SEQUENCE tech_seq_name INCREMENT BY 1; Example SELECT tech_seq_name.nextval FROM dual; ----- 250 ALTER SEQUENCE tech_seq_name INCREMENT BY -250; SELECT tech_seq_name.nextval FROM dual; ALTER SEQUENCE tech_seq_name INCREMENT BY 1;
You can find more on this link
Impact of caching the sequences
Sequences are cached with the purpose of improving the fetch performance. In RAC, each instance stores the cache values
We can have gaps in sequence when using cache due to the following reasons
- Rollback occurs
- System crash or instance crash
- The sequence is used in another table
There is a new feature in Oracle 12c for sequences
Session sequences
CREATE SEQUENCE test_session_seq START WITH 1 INCREMENT BY 1 SESSION;
CREATE SEQUENCE test_global_seq START WITH 1 INCREMENT BY 1 GLOBAL;
| Global | Session |
| creates standard sequence well known in previous release. This is the default. | creates new type session sequence, which is a special type of sequence that is specifically designed to be used with global temporary tables that have session visibility. Session sequence returns a unique range of sequence numbers only within a session, but not across sessions. Another difference is that session sequences are not persistent. If a session goes away, so does the state of the session sequences that were accessed during the session. |
Related Articles
- Primary Key
- Foreign Key
- Unique key
- check constraint
- Not NULL constraint
- Create table oracle
- Alter Table Oracle
- Query to check table size in Oracle
- DROP TABLE
- Oracle Truncate TABLE
- Create Global Temporary Table
- alter table add column oracle
- alter table rename column oracle